Coal
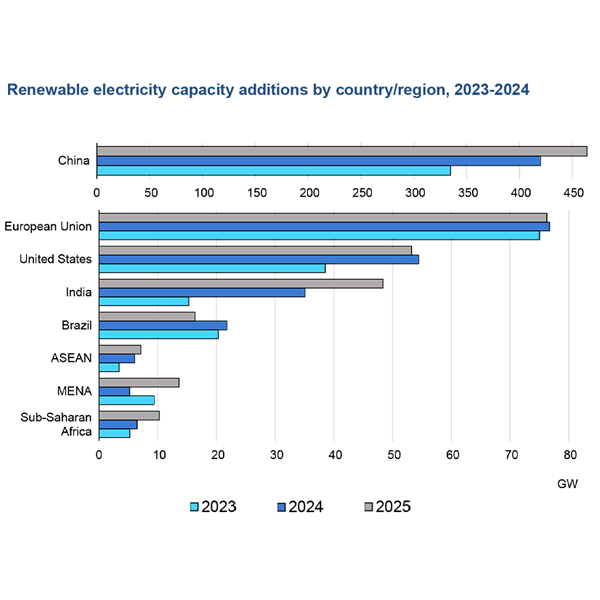
New analyses report record growth for the global renewable energy sector in 2025 and project continued expansion through the end of the decade.
Duke Energy filed its long-range plan with the North Carolina Utilities Commission, calling for more natural gas-fired generation and batteries while keeping existing coal plants online to meet accelerated demand for electricity.
Three cabinet-level agencies announced coordinated policies that are meant to improve coal's position in the energy system by improving power plants, cutting environmental regulations and increasing mining of the fuel.
EPA Administrator Lee Zeldin said the reporting is not mandated under the Clean Air Act, has no bearing on the environment or public health, and imposes hundreds of millions of dollars a year in compliance costs on American businesses.
EPA Administrator Lee Zeldin proudly told NARUC attendees the agency’s proposed rescission of the 2009 endangerment finding would be the “largest deregulatory action in the history of the country.”
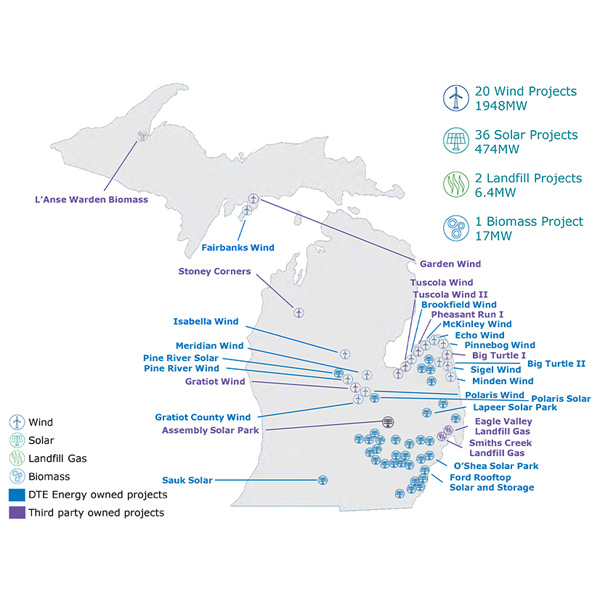
DTE Energy reported it is in various stages of discussion to supply as much as 7 GW to new data centers and is on track to reach agreement on the first project by the end of 2025.
After DOE ignored their rehearing requests, opponents of its Federal Power Act order keeping the J.H. Campbell plant have appealed the issue to the courts.
Industry experts say that while DOE's report points to a well known issue, it focuses only on keeping old plants online instead of needed new capacity.
Georgia Power will add at least 6 GW of new generation capacity by 2031, and potentially as much as 8.5 GW, under its recently approved integrated resource plan.
New technology and energy facilities are planned for Pennsylvania at a cost of more than $90 billion, including multiple power plants and data centers, possibly co-located.
Want more? Advanced Search