U.S. Department of Energy (DOE)
NIPSCO insisted to FERC that a MISO Midwest-wide cost allocation for the continued operation of an Indiana coal plant is the quickest solution.
DOE's senior leadership highlighted how the grid relies on fossil fuels to make it through winter peaks.
A federal order to keep Unit 1 of the coal-fired Craig Generating Station operational past its planned retirement date seems disconnected from grid realities, a Colorado state energy official said.
The U.S. Department of Energy has canceled a pending $1.8 billion loan guarantee to Arizona Public Service that was intended to help finance transmission, renewable energy and storage projects.
State regulators in MISO asked FERC to let power industry stakeholders determine how to allocate the costs for an Indiana coal plant forced to stay online by the Trump administration’s Department of Energy.
U.S. Energy Secretary Chris Wright said the department is ready to use its authority under Section 202(c) of the Federal Power Act to dispatch backup generation from large customers if needed ahead of a major winter storm.
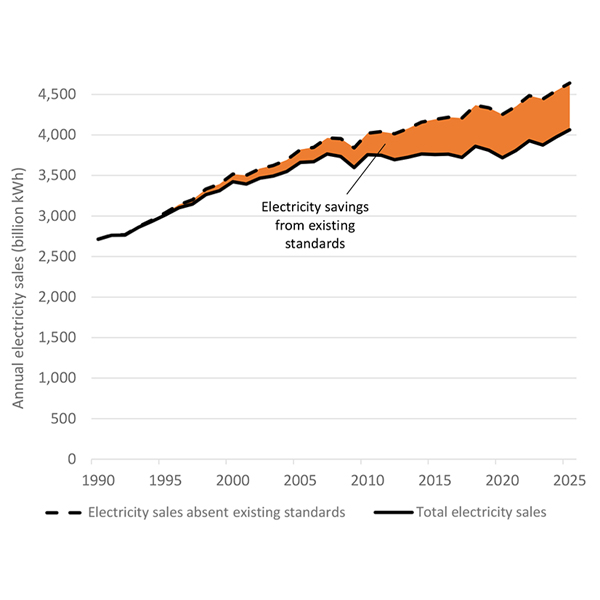
The average U.S. consumer would have spent $6,000 more on utility bills over the past decade without national efficiency standards for appliances, according to a report from the Appliance Standards Awareness Project.
Local elected officials in Colorado are speaking out against the Trump administration’s order to keep the coal-fired Craig Generating Station Unit 1 available to operate past its planned retirement date.
Washington’s attorney general and a coalition of environmental groups have mounted separate challenges to DOE's December decision to order TransAlta to continue operating the state’s last coal-fired plant for three months beyond its scheduled retirement.
Democrats pressed a senior DOE official on recent decisions affecting PJM, including the agency's orders to keep coal plants running, while another agency shut down offshore wind projects nearing completion.
Want more? Advanced Search