Resource Adequacy
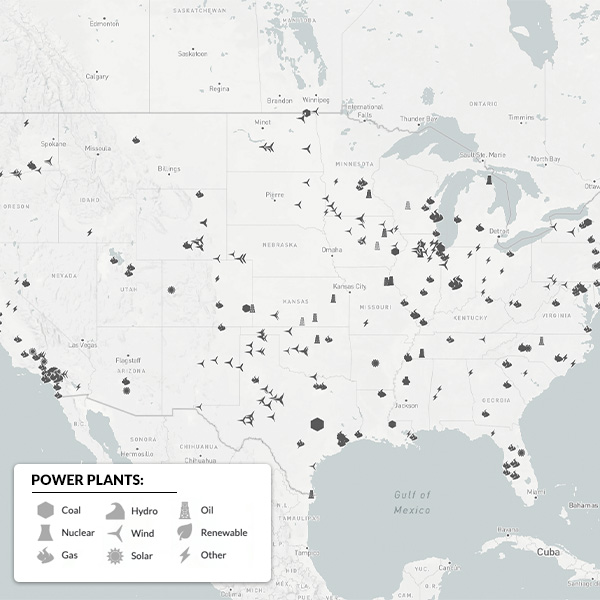
Resource adequacy is the ability of electric grid operators to supply enough electricity at the right locations, using current capacity and reserves, to meet demand. It is expressed as the probability of an outage due to insufficient capacity.
Coordination between the gas and electric industries is becoming increasingly crucial to meet demand and to tackle extreme weather events, panelists participating in a WECC webinar argued.
Industry experts say that while DOE's report points to a well known issue, it focuses only on keeping old plants online instead of needed new capacity.
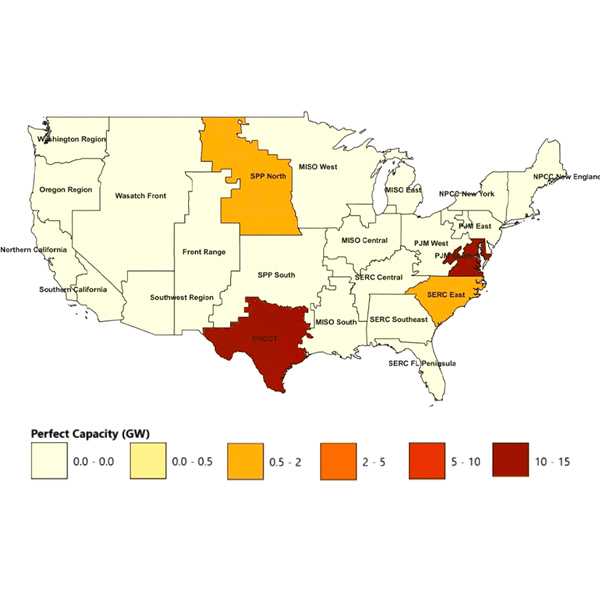
DOE's report tries to apply one reliability metric to different markets and finds significant new capacity will be needed in some markets to avoid reliability problems by 2030.
NERC Chief Engineer Mark Lauby said the North American grid already has measures in place to prevent the mishaps that led to April's blackout in Spain and Portugal.
Analysis from a Grid Strategies expert indicates that the issues that caused the Iberian Peninsula blackout are unlikely to occur in the U.S.
The Michigan attorney general and a group of 10 NGOs have filed for rehearing of DOE's order to keep a coal plant running for this summer, while those parties and others debated the cost recovery filing Consumers Energy made at FERC.
NERC acknowledges it used mismatched data to calculate MISO's risk level in its Long-Term Reliability Assessment and plans to release a revised report soon.
In a webinar, ReliabilityFirst staff discussed Germany's difficulties meeting electric demand in recent years and lessons for U.S. utilities.
The Texas Reliability Entity has added key risks related to artificial intelligence and large loads as part of its annual reliability and regional risk assessment of the ERCOT grid.
NERC released its State of Reliability report, which found the bulk power system remains highly reliable and underlying performance metrics such as frequency response and misoperation rates are improving or remain stable.
Want more? Advanced Search