IESO
Ontario’s Independent Electricity System Operator is a government organization with a mixture of commercial and public-policy goals, owned by the government of Ontario. It was created to prepare for deregulation of the province’s electrical system and is governed by a board whose directors are appointed by the provincial government.
Stakeholders mostly said the recommendations to update NERC's standards development process represented a good start but needed further development to ensure a fair process.
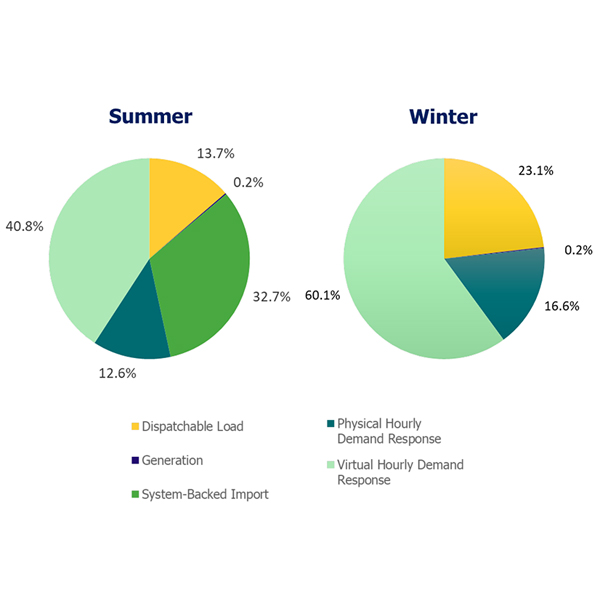
IESO is reconsidering how it deploys hourly demand response following complaints over partial activations and an increase in standby notices.
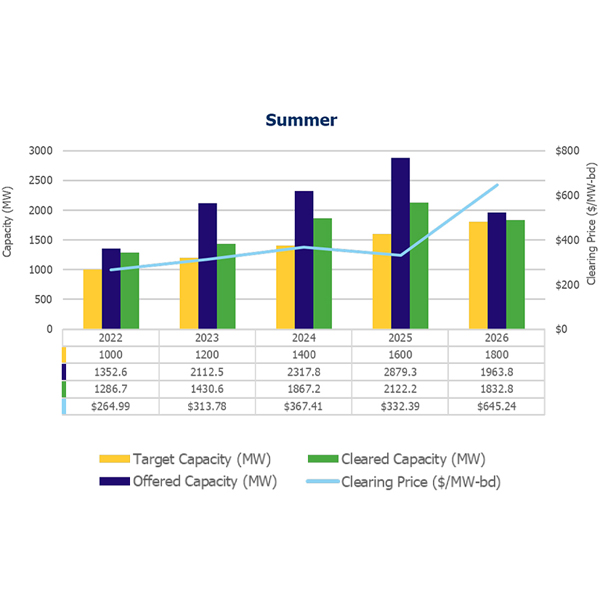
IESO downgraded less than 100 MW of capacity for November’s auction in the first application of its Performance Adjustment Factor in both the winter and summer seasons.
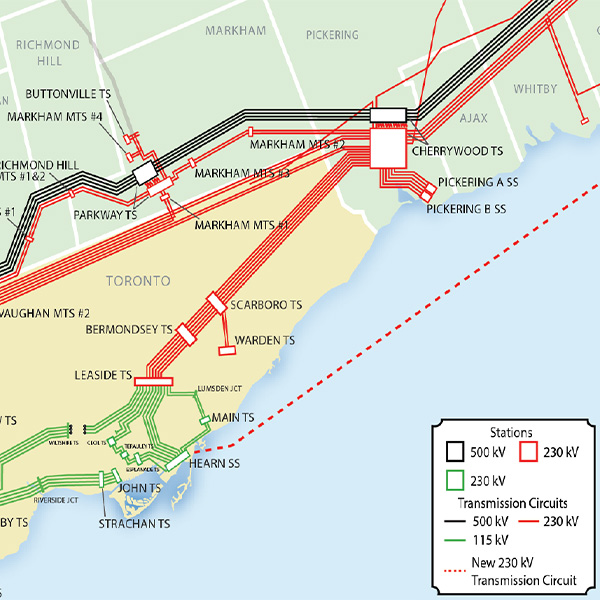
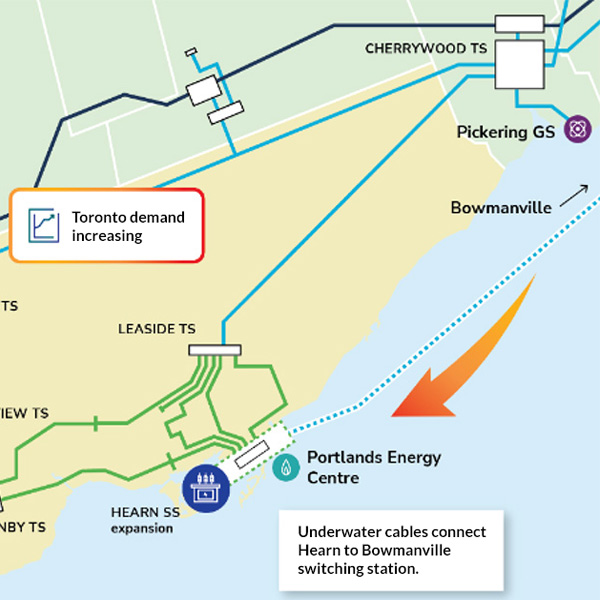
IESO is seeking stakeholder input on its first competitive transmission solicitation: a $1.5 billion HVDC line under Lake Ontario that will become the third major supply line for Toronto.
IESO officials held firm on excluding hydro redevelopment projects from the ISO’s Long Lead-Time procurement despite objections from potential bidders.
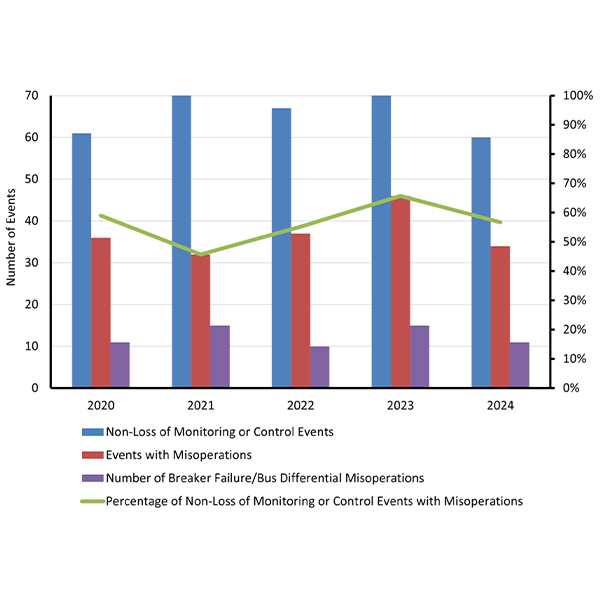
IESO is targeting six areas of NERC’s Reliability Standards in its 2026 compliance program, largely continuing a focus on issues it has prioritized since 2023.
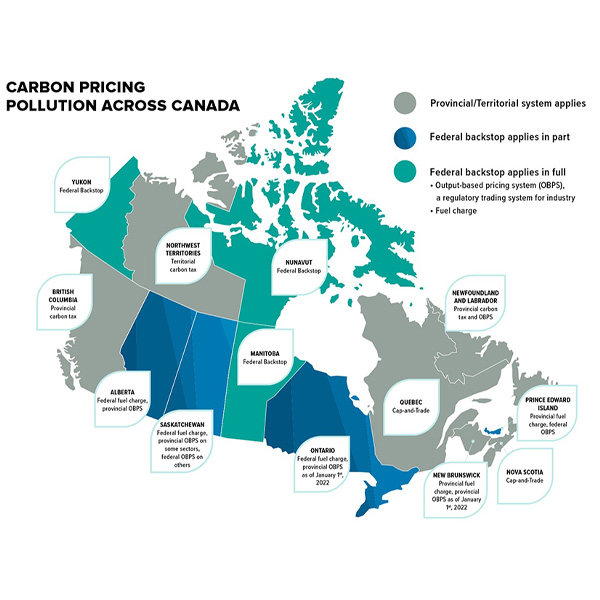
After scrapping most Trudeau-era climate policies, Prime Minister Mark Carney wants to tighten rules over Canada’s industrial carbon markets, which observers say have failed to incentivize emission reductions.
Ontario approved IESO’s proposed $1.5 billion HVDC line under Lake Ontario, which planners say is needed to meet a potential doubling of Toronto’s electricity demand by 2050.
IESO's latest Reliability Outlook reduces its 2026 demand growth projection slightly, citing “international trade tensions.”
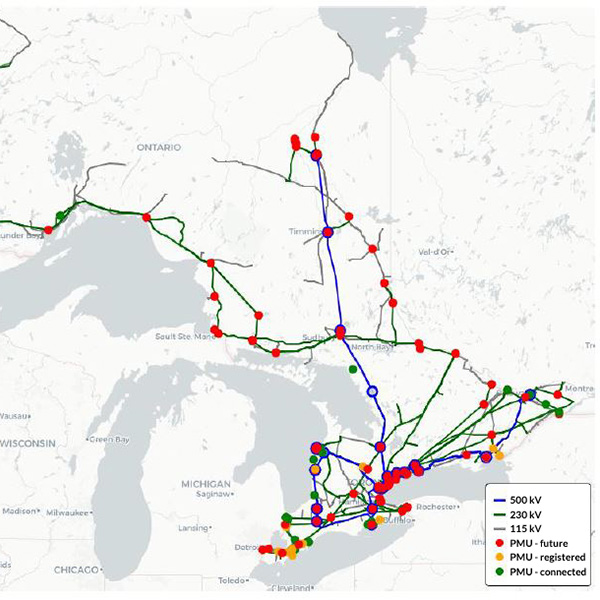
IESO released proposed market rule and manual revisions to require synchrophasor data from storage resources.
Want more? Advanced Search