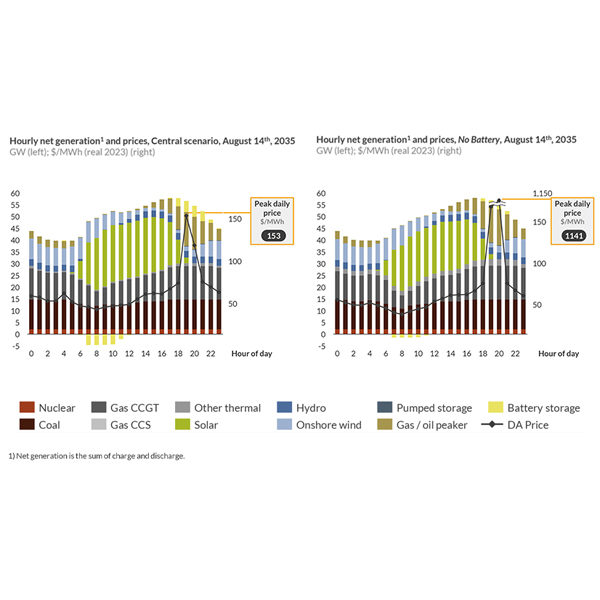
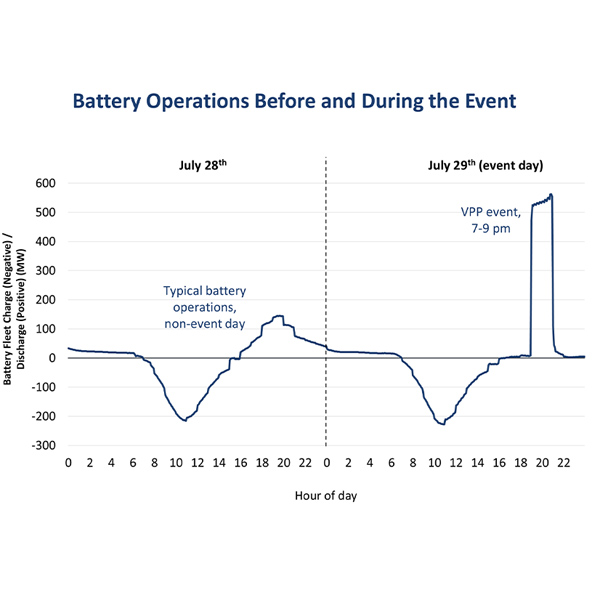
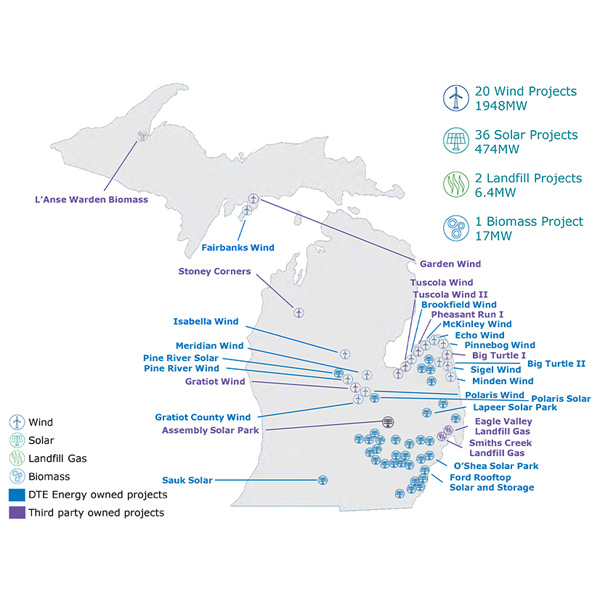
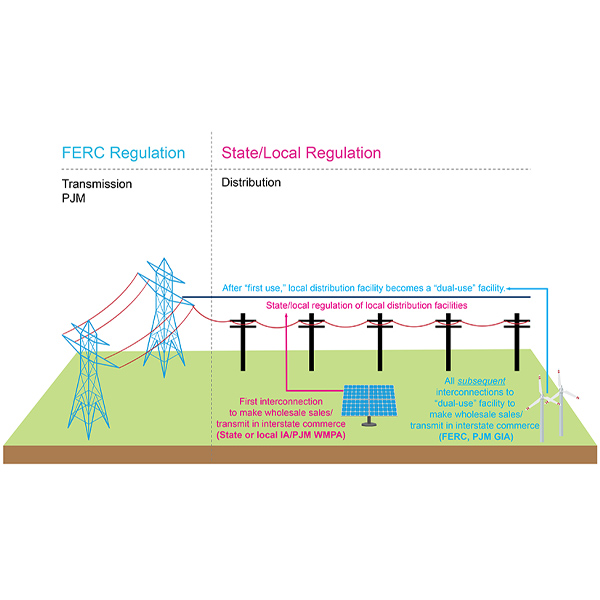
Battery Electric Storage
At a recent Budget and Priorities Working Group meeting, NYISO presented its final recommendations for 2026, which will define where the ISO puts its market design resources.
Investment bank Jefferies’ latest analysis finds the levelized cost of paired solar-plus-battery storage is cheaper than that of gas, saying slow turbine deliveries and inflationary equipment pricing makes the renewable alternative an “attractive” opportunity as data centers drive demand.
CAISO’s Market Monitor is concerned about potential gaming practices and inefficient bidding behavior in the ISO’s bid cost recovery process for battery storage resources.
A new report urges SPP to accelerate its interconnection process and reform market rules to allow greater buildout of energy storage.
The growing number of data centers offers a major growth opportunity for demand response, as it can help get the energy-hungry facilities online quicker than new generation, speakers said at CPower Energy’s GridFuture 2025 conference.
Colorado regulators have approved Tri-State Generation and Transmission Association’s plan to add 1,657 MW of new resources from 2026 to 2031, despite objections about the inclusion of a new natural gas plant.
An aggregation of more than 100,000 residential batteries provided an average 535 MW of support to California’s electricity grid during a test to prepare for the hot summer period ahead.
DTE Energy reported it is in various stages of discussion to supply as much as 7 GW to new data centers and is on track to reach agreement on the first project by the end of 2025.
PJM's Markets and Reliability Committee endorsed by acclamation an issue charge by Constellation Energy focused on how storage as a transmission asset could be implemented in the RTO.
IESO opened discussions on new rules for storage facilities and hybrid resources that will enable the provision of regulation service.
Want more? Advanced Search