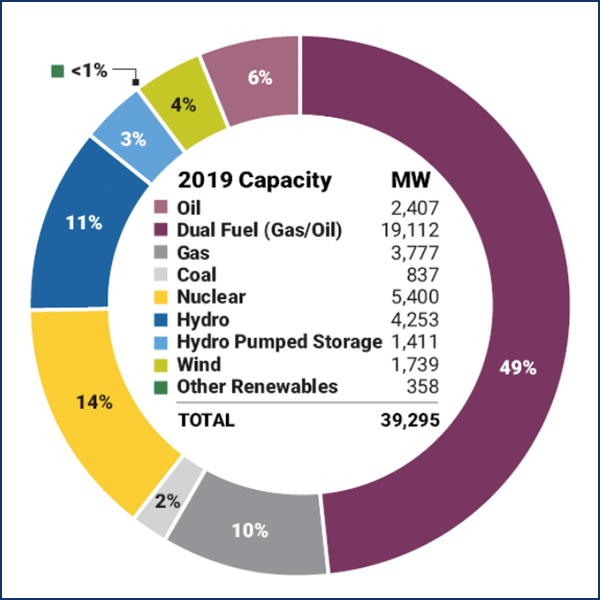
Resource Adequacy
Resource adequacy is the ability of electric grid operators to supply enough electricity at the right locations, using current capacity and reserves, to meet demand. It is expressed as the probability of an outage due to insufficient capacity.
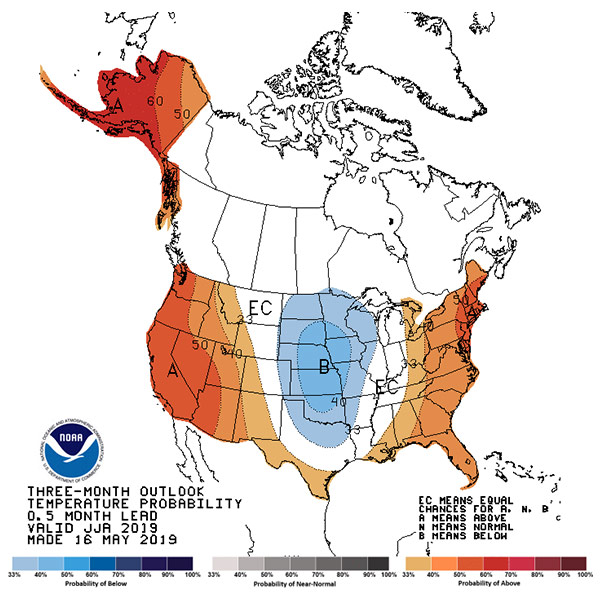
NYISO said it expects to have adequate resources on hand to meet slightly above-normal demand this summer, with 42,056 MW of capacity available.
ERCOT in April set new monthly generation records for its wind and solar fleets, producing 7,148 GWh and 408 GWh, respectively.
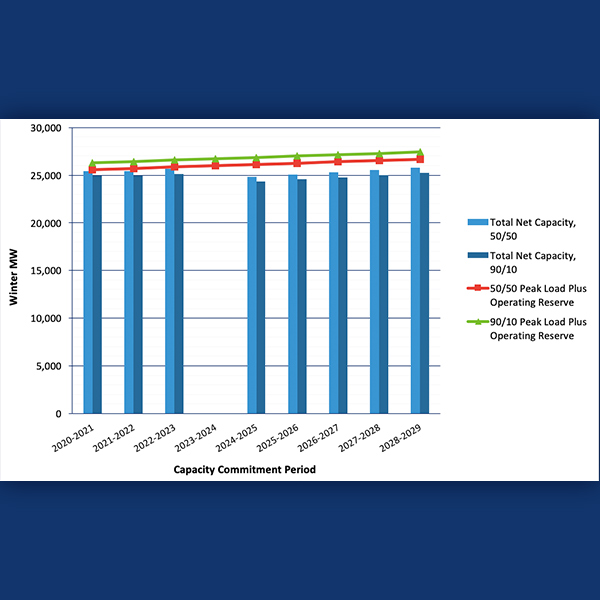
ISO-NE projects net installed capacity requirements will increase and procedures could be needed to overcome a shortage of “operable” capacity.
NYISO’s Management Committee recommended the Board of Directors approve a Comprehensive Reliability Plan that pointed to potential risks that could develop.
FERC has agreed to New England’s request for a public “prefiling” meeting to discuss the region’s plans for long-term fuel security.
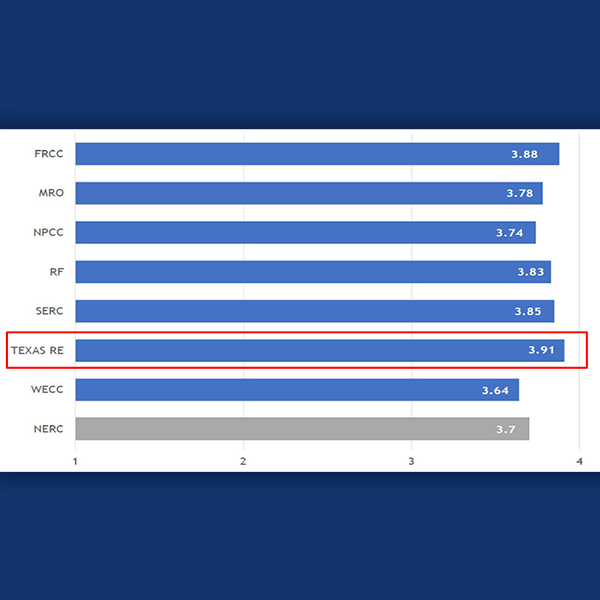
The Texas Reliability Entity bested all other REs on NERC’s 2018 ERO effectiveness survey, the RE's Board of Directors heard.
ERCOT’s low reserve margin sticks out when compared to those of most other regions in the U.S., where their reserves are well above their reference levels.
CAISO’s summer load forecast predicts an abundance of hydroelectric power but sees constraints on its natural gas supplies.
The Texas Public Utility Commission gave its final blessing to a $1.37 billion transaction involving Oncor, Sharyland Utilities and Sempra Energy.
MISO want to improve how owners of LMRs interact with a communications system that some think hampered the RTO’s response to a grid emergency this winter.
Want more? Advanced Search