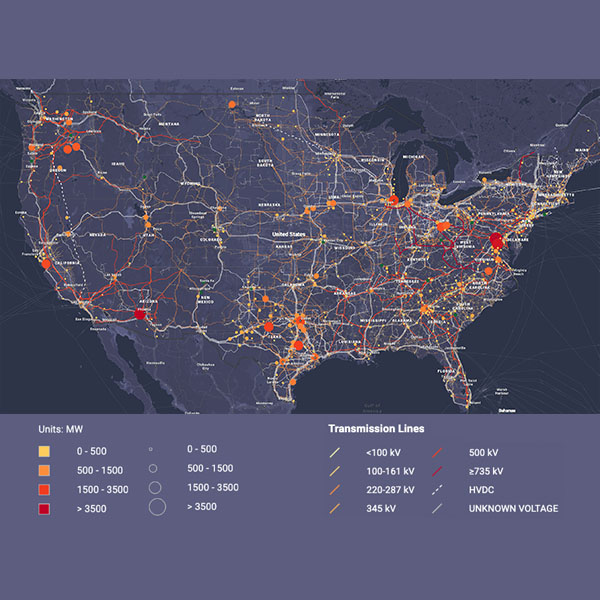
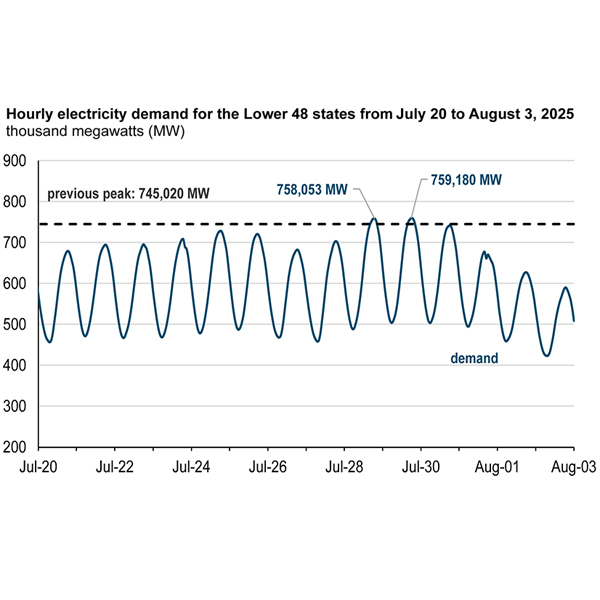
Resource Adequacy
Resource adequacy is the ability of electric grid operators to supply enough electricity at the right locations, using current capacity and reserves, to meet demand. It is expressed as the probability of an outage due to insufficient capacity.
The U.S. Department of Energy is kicking off its Speed to Power initiative by seeking input on large-scale grid projects that would serve large-scale data centers.
The bipartisan Problem Solvers Caucus introduced a framework it hopes can lead to permitting legislation this session.
Texas regulators proposed new rules on large load forecasting criteria and net metering following the state’s recent biennial legislative session and opened them up to public comment.
CAISO is finalizing a set of changes to its resource adequacy program, with plans to vote on three proposals at an upcoming Board of Governors meeting,
FERC focused on large loads and clearing out older proceedings during its September meeting, with two of three current members saying they hoped to move a pending proceeding on co-located loads in the near future.
MISO said 2025 was the most demanding summer since 2012, though it steered the grid with only a single maximum generation event.
PJM revised elements of its proposal to create a non-capacity backed load product for large loads as the Critical Issue Fast Path embarks on determining how to address the reliability challenges posed by accelerating data center load growth.
Ontario environmental groups panned the Canadian government’s inclusion of small modular reactors among infrastructure projects selected to receive fast-track regulatory treatment, saying renewables would be a far cheaper way to expand generation capacity.
Heat affects the full length of the electric supply chain: from generation, through the grid, to utilities’ customers, says columnist Dej Knuckey.
The Pacific Northwest is on track to meet energy efficiency goals set in the Northwest Power and Conservation Council’s 2021 power plan after having saved 160 aMW through improvements in 2024, the council said in a news release.
Want more? Advanced Search