Resource Adequacy
Resource adequacy is the ability of electric grid operators to supply enough electricity at the right locations, using current capacity and reserves, to meet demand. It is expressed as the probability of an outage due to insufficient capacity.
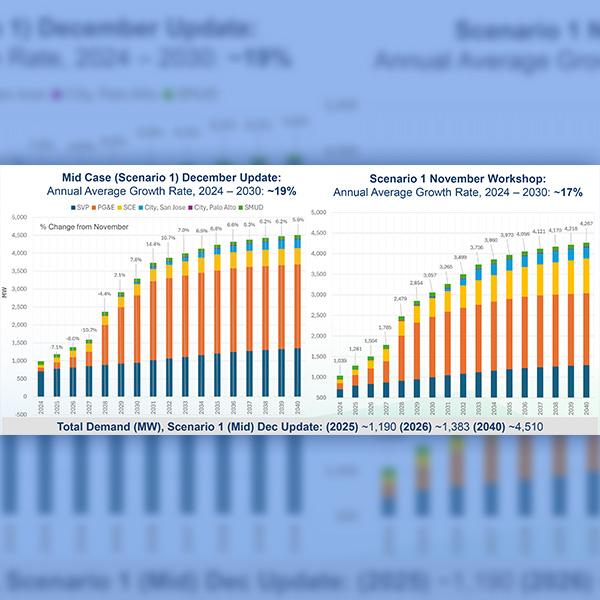
The California Energy Commission has updated its energy demand forecast for data centers after receiving revised figures from Pacific Gas and Electric about data center growth.
Texas regulators shelved the market design they once favored, agreeing with staff's recommendation that the performance credit mechanism results in “minimal” additional resource adequacy value.
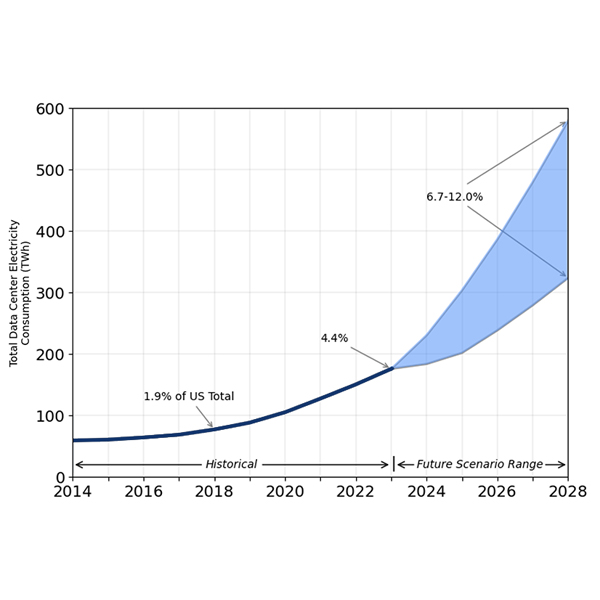
Data centers’ voracious appetite for electricity could spike more than threefold over the next four years, rising from 4.4% of U.S. power demand in 2023 to as high as 12% in 2028, according to the Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory.
MISO said it will finalize an availability-based accreditation for nearly 12 GW of load-modifying resources over the first quarter of 2025 ahead of a filing with FERC.
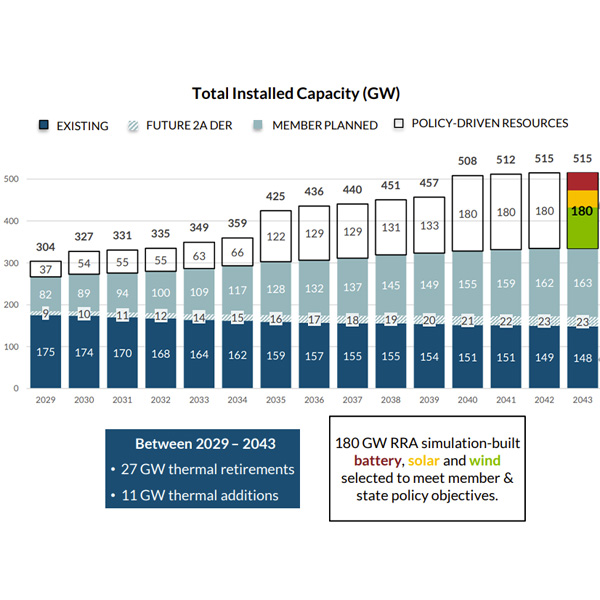
MISO said members must add an “unprecedented” 17 GW in new resources annually over the next two decades to reliably meet demand and decarbonization goals.
Vistra is extending the life of its coal-fired Baldwin Power Plant in Illinois through 2027 amid MISO delivering warnings over a supply crunch in its footprint.
The Virginia State Corporation Commission spent a full day looking at how growing demand from data centers is impacting the commonwealth's electric grid and rates.
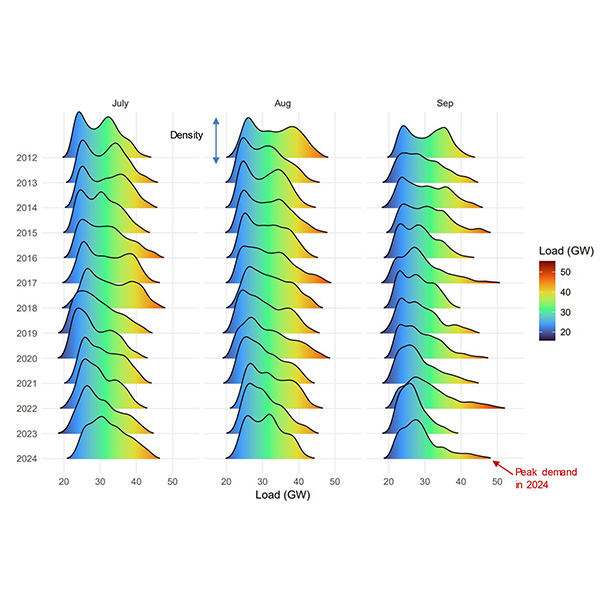
CAISO's Department of Market Monitoring reported that the ISO saw “one of the highest demand peaks” in recent years in 2024.
MISO President Clair Moeller predicted MISO will face a few tough years before securing enough generation to tame load growth and fashioning operational tools that help subdue the volatility of renewable energy.
MISO told its Board of Directors that drafting an interconnection queue express lane for generators that resolves resource adequacy risks and has stamps of approval from regulators is essential.
Want more? Advanced Search