Federal Energy Regulatory Commission (FERC)
The Federal Energy Regulatory Commission is an independent agency that regulates the interstate transmission of electricity, natural gas and oil; reviews proposals to build LNG terminals and interstate natural gas pipelines; and licenses hydropower projects. FERC also oversees operations of regional wholesale electricity and natural gas markets and oversees the reliability of the bulk electric system.
If ex-FERC Commissioner Bernard McNamee has his way, the next president will eliminate the federal government’s climate programs and have FERC “reexamine” RTOs.
NYISO gave initial comments and reactions to FERC Order 2023, but remained reluctant to divulge too much during its TPAS meeting.
The D.C. Circuit denied a petition to review FERC’s approval of SPP’s tariff revisions setting up a uniform planning criteria in each transmission zone to evaluate zonal reliability upgrades.
FERC’s revamp of its generator interconnection procedures will impose penalties on transmission providers that fail to complete studies on time.
The chairs of NAESB's forum on gas-electric harmonization said significant reforms may be needed to bring the two industries into alignment.
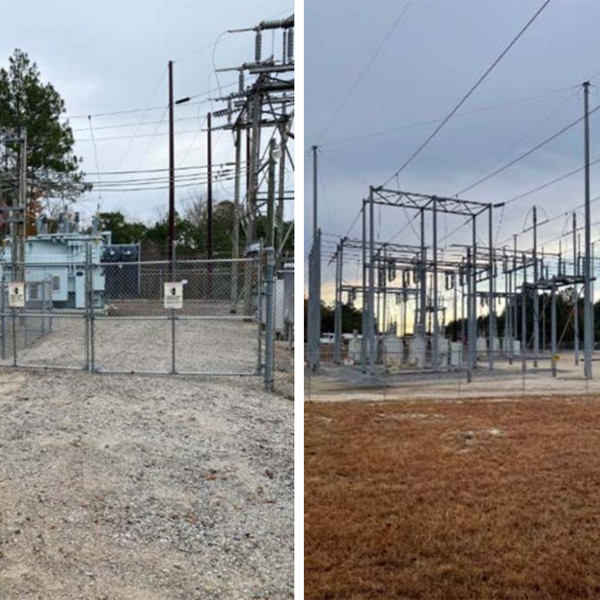
FERC approved Niagara Mohawk Power's construction recovery requests for the Smart Path Connect project and partly accepted its rate schedule revisions.
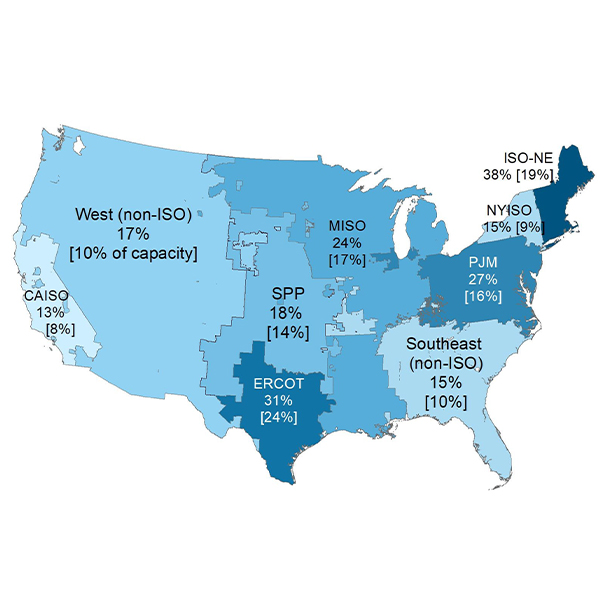
FERC approved Order 2023 at its regular meeting, requiring changes to its pro forma interconnection queue that are aimed at clearing up the backlog of more than 2,000 GW of resources.
The D.C. Circuit Court of Appeals denied a pair of petitions by Green Development over FERC’s approval of transmission charges connected to a proposed solar project.
SPP's legal staff is evaluating its options after FERC's recent rejection of a tariff revision to allocate “byway” transmission projects on a case-by-case basis.
FERC rejected a call for new physical security standards while clarifying its cybersecurity incentives order.
Want more? Advanced Search