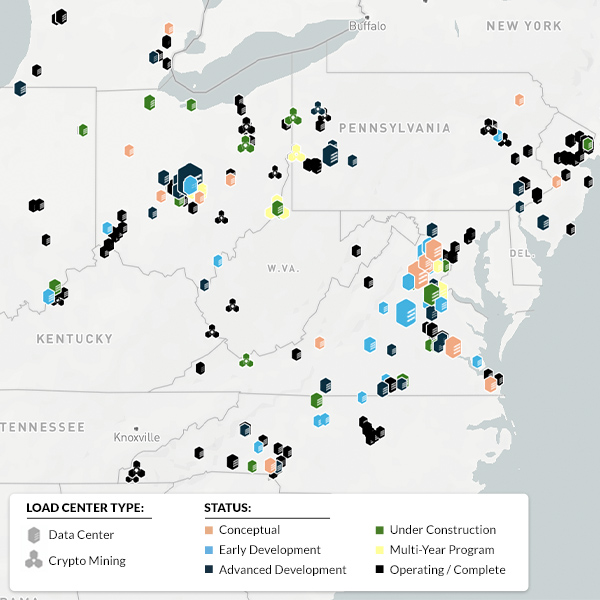
load-serving entities (LSEs)
FERC denied rehearing requests regarding approved revisions to CAISO’s Open Access Transmission Tariff generator interconnection procedures, which contesting parties said rely on in part on “subjective and discriminatory criteria.”
Comments about FERC's technical conference argued for a variety of reforms to address resource adequacy.
MISO stakeholders are skeptical of the RTO’s proposed new approach to divvying up reliability obligations among load-serving entities based on evolving system risk.
MISO’s proposal to use a temporary “fast lane” in its interconnection queue to speed up necessary resource additions would give utility-owned generation preferential treatment, according to protesters’ comments filed with FERC.
MISO hopes to mete out different reserve margin obligations to its load-serving entities as it sees bigger perils on the horizon.
Load-serving entities that decide against participating in MISO’s capacity auction must secure anywhere from 1.5% to 4.2% beyond their reserve margin requirements in the 2025/26 planning year.
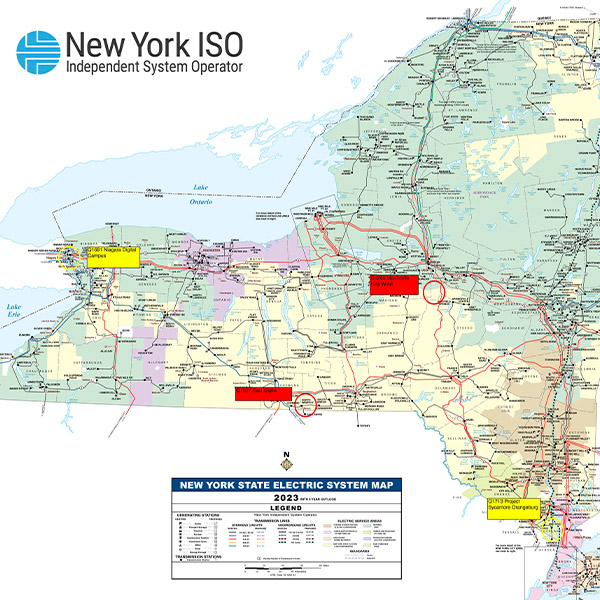
The New York Department of Public Service presented a proposal for updating the method by which NYISO determines peak load hours to the ISO’s Installed Capacity Working Group.
FERC approved CAISO's proposal to streamline its generator interconnection process to deal with the “unprecedented volume” of interconnection requests it received in 2023.
A financial consulting firm said that MISO’s auction revenue rights and financial transmission rights market needs updating to keep up with the changing grid.
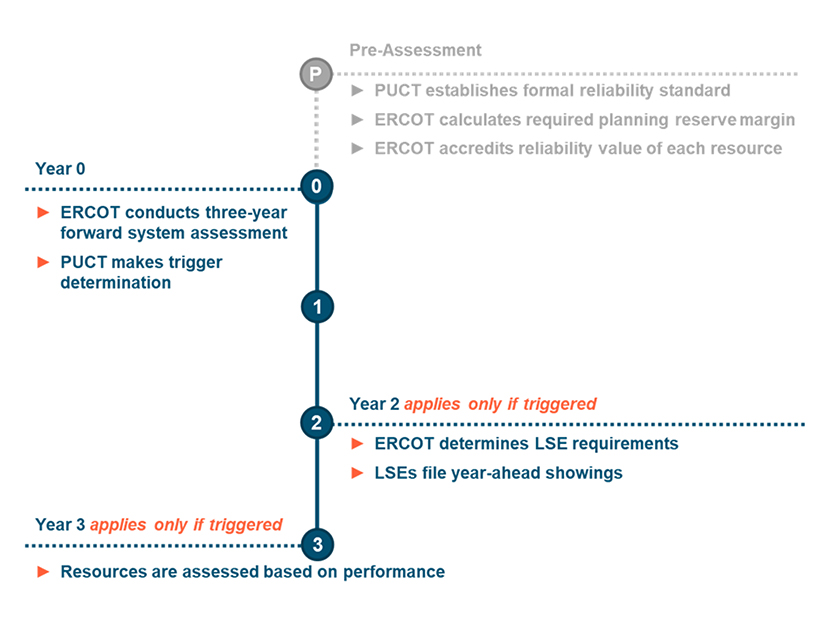
A new white paper proposes creating an LSE Reliability Obligation in ERCOT that would assign Texas utilities a certain amount of capacity to maintain.
Want more? Advanced Search