Resource Adequacy
Resource adequacy is the ability of electric grid operators to supply enough electricity at the right locations, using current capacity and reserves, to meet demand. It is expressed as the probability of an outage due to insufficient capacity.
FERC spent June 4-5 looking into resource adequacy across the markets it regulates.
NPCC's Summer Reliability Assessment found that the region generally has enough resources to meet demand this summer, though weather patterns could strain grid operators.
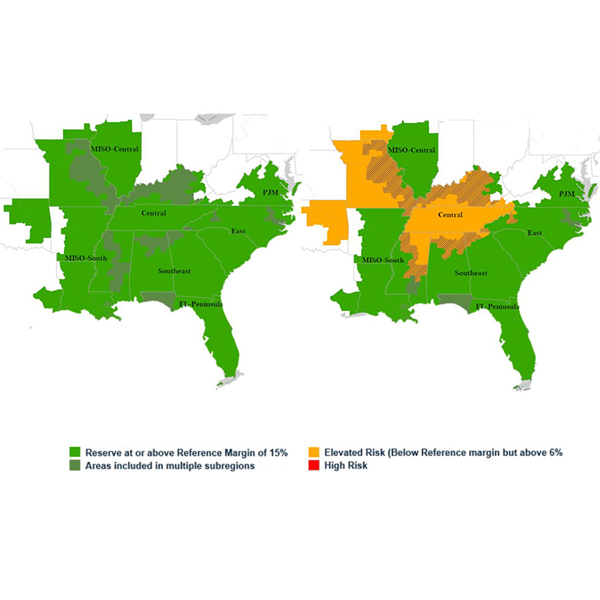
SERC said all subregions should have enough resources to handle normal summer conditions, but the Central subregion may see energy shortfalls during periods of extreme heat.
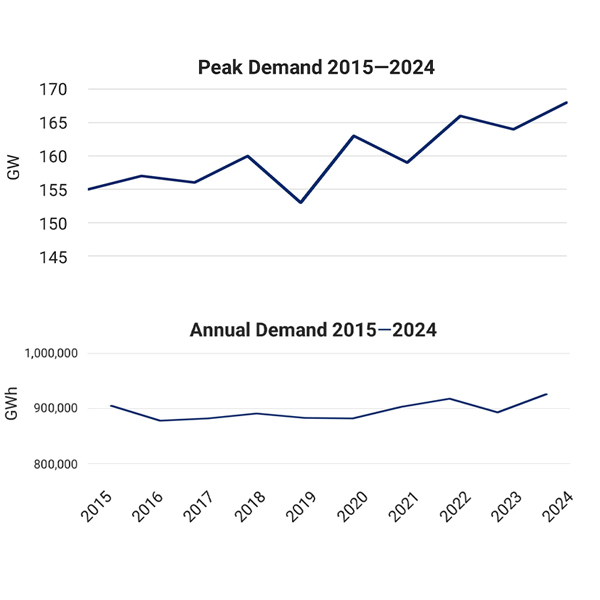
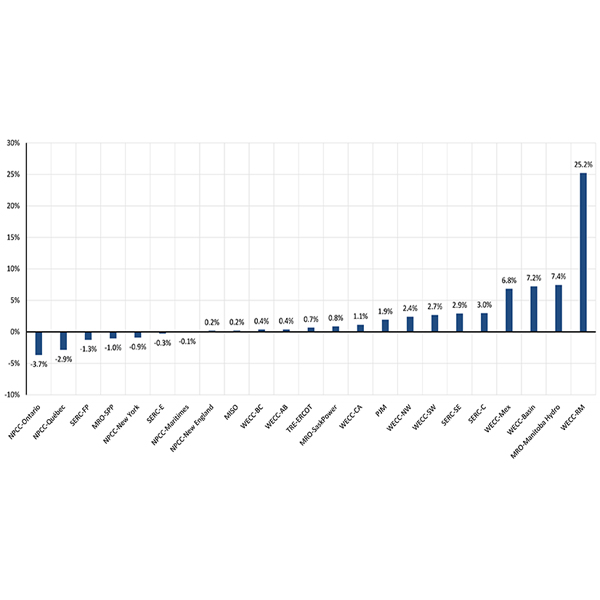
Peak demand in the Western Interconnection hit a record high of 168.2 GW in 2024, reflecting “early effects” of the growth in large loads such as data centers, according to a new WECC report.
President Donald Trump’s policies and the growth in demand from data centers and other new customers have changed the trajectory of the power system, speakers said at the Energy Future Forum.
Experts in the data center field discussed the challenges of meeting accelerating computational load during the PJM Annual Meeting, held in the core of Northern Virginia’s Data Center Alley.
Former FERC Chair Neil Chatterjee and other panelists in an ACORE-hosted webinar warned that grid stakeholders need to put aside old ways of thinking to address growing reliability challenges.
FERC's summer assessment shows rising demand and prompted Chair Mark Christie to discuss recent developments in PJM.
Texas Reliability Entity CEO Jim Albright sees similarities between the issues facing the U.S. and European grid and hopes to learn from the recent Iberian Peninsula outage.
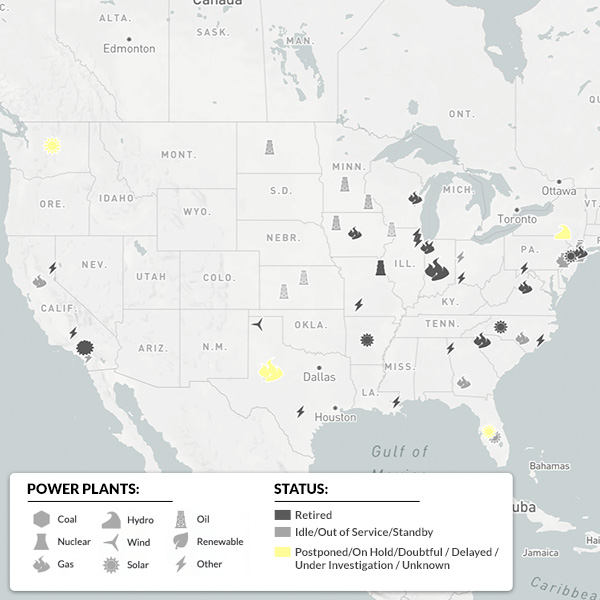
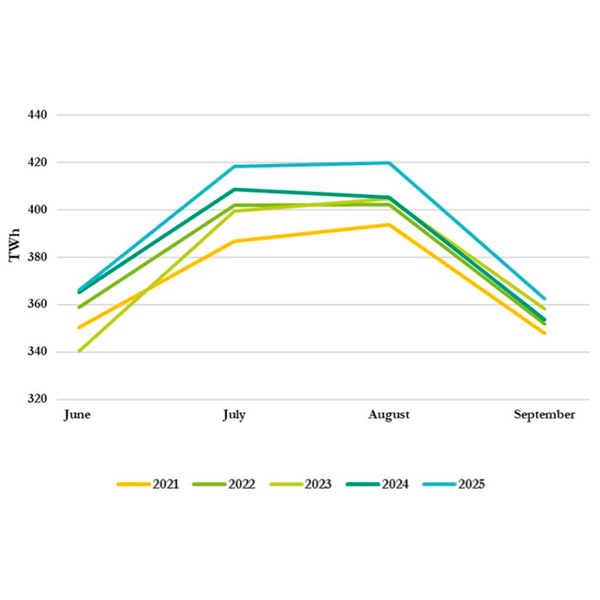
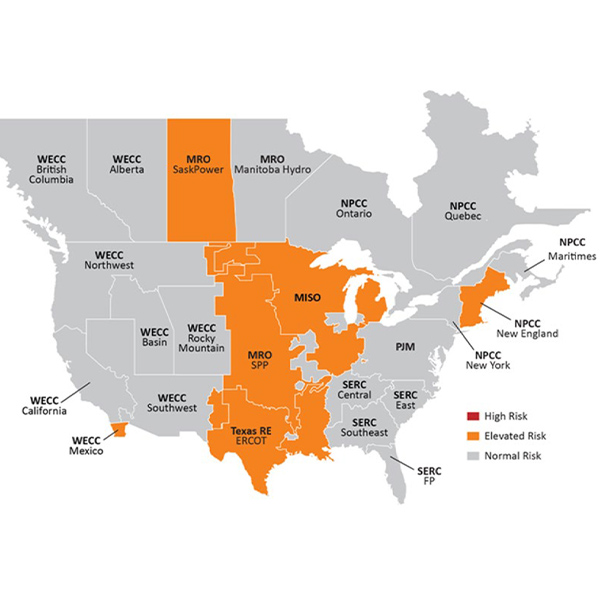
NERC's Summer Reliability Assessment found that energy shortfalls are possible this summer in the middle of North America, New England and Baja California.
Want more? Advanced Search