FERC & Federal
The Federal Energy Regulatory Commission is an independent regulatory agency that oversees the transmission of electricity, natural gas and oil in interstate commerce, as well as regulating hydroelectric dams and natural gas facilities.
DOE’s latest assessment of transmission congestion has concluded there is no need to designate national-interest transmission corridors.
Commenters generally back FERC’s proposal to approve new NAESB standards for transmission but urged it to reject two replacement rules.
After a three-month delay because of the pandemic, CIP-013-1 took effect, starting the 18-month compliance period for stakeholders.
FERC accepted proposed revisions to seven NERC reliability standards, as well as the ERO Enterprise's business plans and budget for 2021.
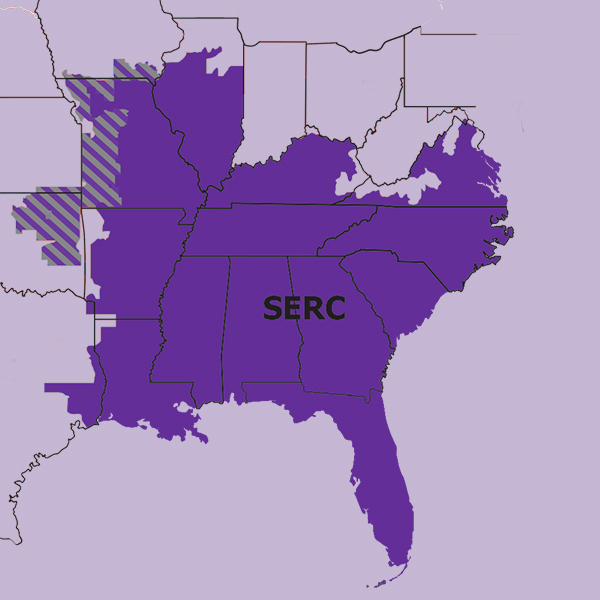
FERC approved a settlement between SERC Reliability and Associated Electric Cooperative Inc. for violations of NERC reliability standards.
DOJ brought criminal charges against six Russian intelligence officers believed to be involved in the cyberattacks against the Ukrainian grid.
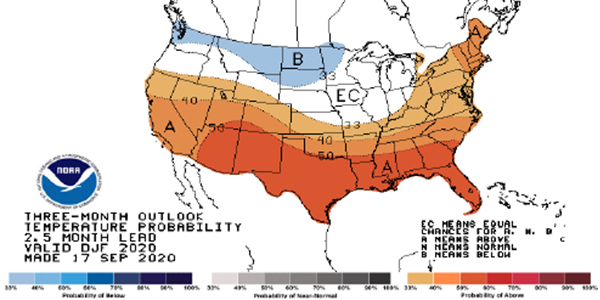
FERC staff expressed confidence that the North American bulk power system has sufficient reserves to make it through the winter comfortably.
FERC gave WECC the go-ahead to introduce a new version of its reliability standard regarding contingency reserves.
Despite actions on supply chain risk management, changes are still needed to grapple with foreign cyber threats to the utility sector.
In its latest round of CIP audits, FERC noted several “potential compliance infractions” and other areas for improvement.
Want more? Advanced Search