Battery Electric Storage
A California PUC judge has proposed the commission order an additional 6 GW of capacity for the state between 2029 and 2032 to get ahead of disappearing federal tax credits and loans for renewable energy resources.
Duke Energy filed its long-range plan with the North Carolina Utilities Commission, calling for more natural gas-fired generation and batteries while keeping existing coal plants online to meet accelerated demand for electricity.
The California PUC is recommending the state build an additional 68.5 GW of new solar generation resources by 2045, despite new tariffs on imports and the planned elimination of federal tax credits.
The U.S. Department of Energy is looking for developers that want to build artificial intelligence data centers — and the power generation to run them — on two nuclear sites.
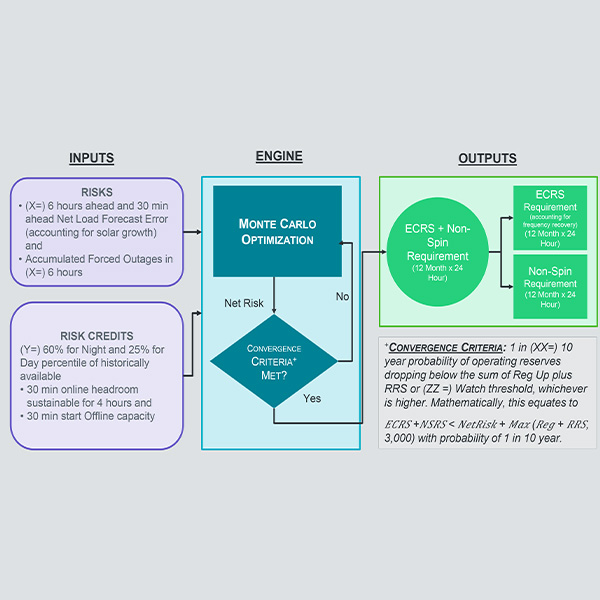
ERCOT’s Board of Directors approved staff’s recommended methodologies for acquiring minimum ancillary service requirements in 2026, despite concerns over conservative operations and target procurement levels.
IESO has increased the capacity target for its planned solicitation for long lead-time resources, even as it acknowledges questions about the need for the procurement.
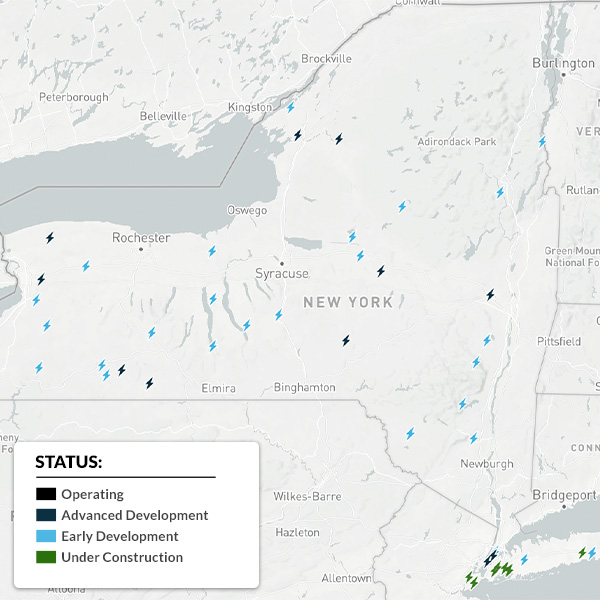
Debates over battery energy storage systems are playing out in towns and cities across New York as the state pursues its goal of 6 GW of energy storage by 2030.
The D.C. Circuit Court of Appeals upheld an earlier decision that sided with FERC on a PURPA case without using Chevron deference, agreeing with the commission's statutory interpretation.
A new study looking at the business case for comparable behind-the-meter and front-of-the-meter battery storage systems in Massachusetts found that FTM storage “significantly outperformed” the BTM systems, despite significant programs and incentives supporting BTM storage in the state.
ERCOT stakeholders at the Infocast Texas Clean Energy Summit discussed tariff trade wars, supply chain issues, data centers and the latest biennial legislative session in Texas that concluded with Senate Bill 6.
Want more? Advanced Search