Resource Adequacy
Resource adequacy is the ability of electric grid operators to supply enough electricity at the right locations, using current capacity and reserves, to meet demand. It is expressed as the probability of an outage due to insufficient capacity.
MISO staff and the Independent Market Monitor agreed that the surge in MISO South outages are troubling and should be addressed.
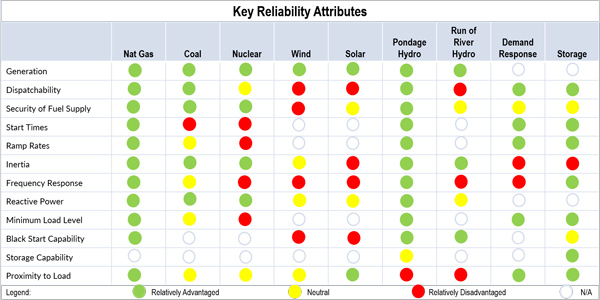
A study released by the American Petroleum Institute said policy makers should seek “reliability attributes,” which natural gas is “relatively advantaged” in.
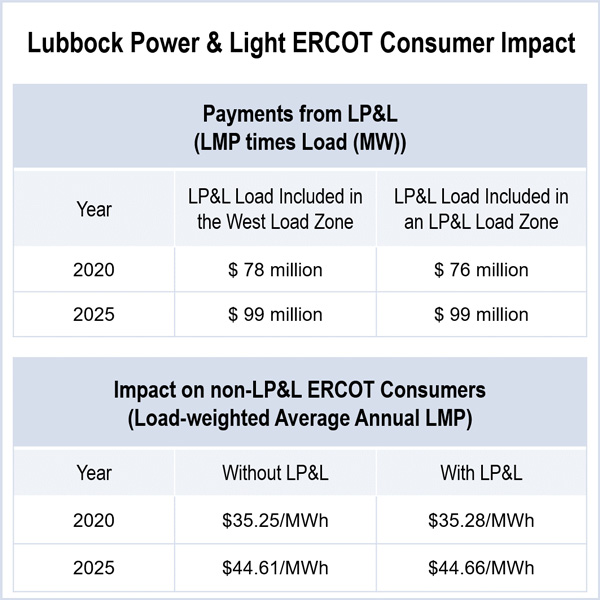
The ERCOT board learned that Lubbock Power & Light’s potential transition from SPP could result in as much as $77 million in increased production costs.
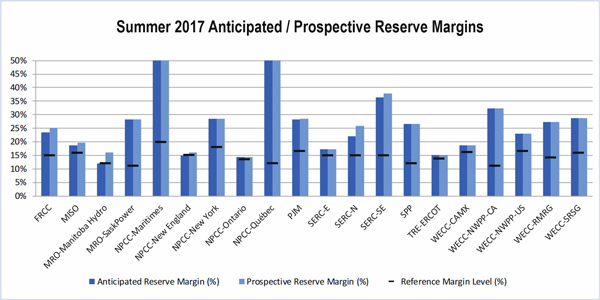
Planning reserve margins are expected to be adequate for a hotter-than-normal summer, FERC said in its annual summer reliability report.
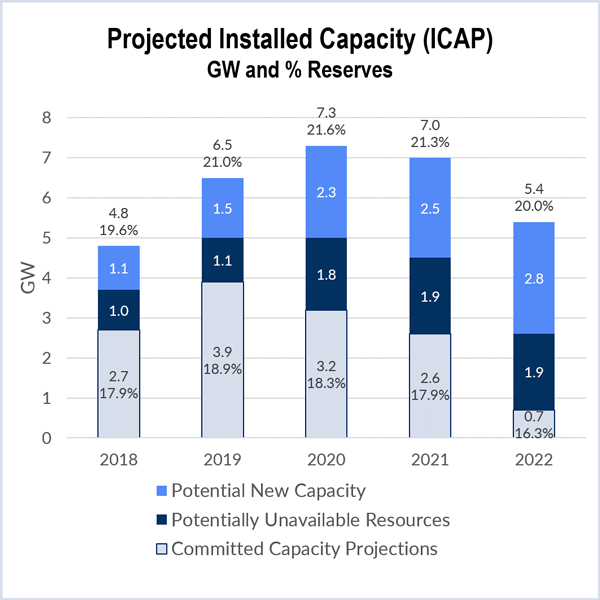
The 2017 Organization of MISO States (OMS) - MISO resource adequacy survey suggests the RTO will have sufficient capacity to meet near-term planning requirements.
The NYISO Management Committee discussed the upcoming summer, an annual review of the Market Monitoring Unit and Tariff changes.
SPP stakeholders approved a revision request that allows the RTO to lower its planning reserve margin as it waits on a quorum-less FERC.
President Trump followed through on his campaign pledge to withdraw the U.S. from the Paris Climate Accord on climate change
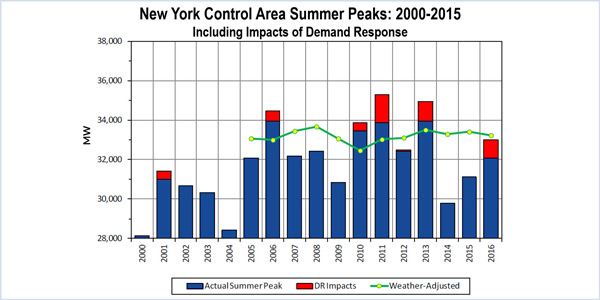
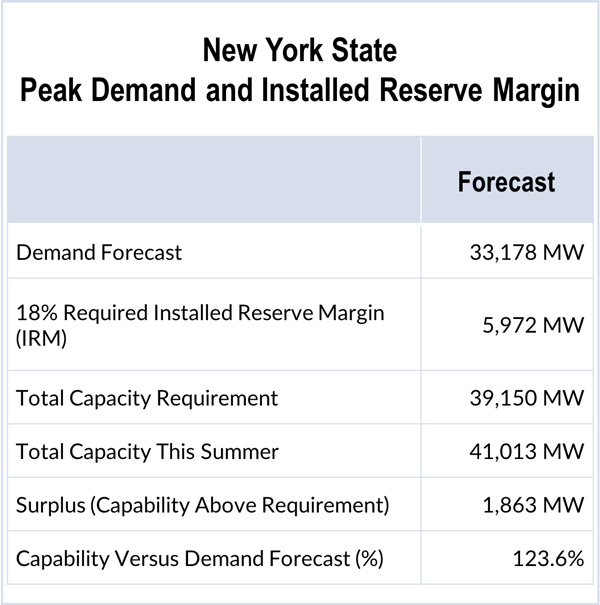
The New York Public Service Commission (NYPSC) said the state’s utilities have 41 GW of capacity, more than enough to meet a projected peak summer load.
CAISO stakeholders voiced skepticism about the effectiveness of a new ISO initiative to prevent early retirement of unprofitable generators.
Want more? Advanced Search