Resource Adequacy
Resource adequacy is the ability of electric grid operators to supply enough electricity at the right locations, using current capacity and reserves, to meet demand. It is expressed as the probability of an outage due to insufficient capacity.
MISO and its Independent Market Monitor have reconciled their differences and reached a compromise on the RTO's capacity market design.
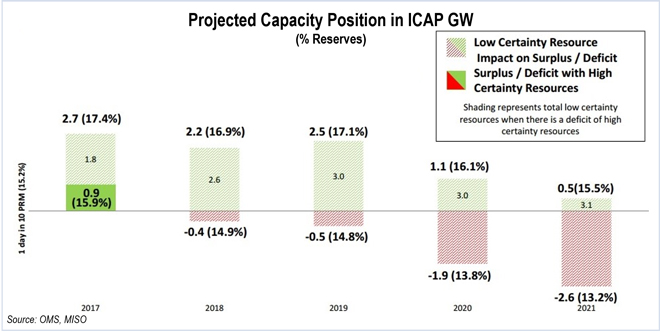
The MISO-OMS 2016 Survey found that plant retirements could cause a generation shortfall as early as 2018 in MISO, 2 years earlier than previously expected.
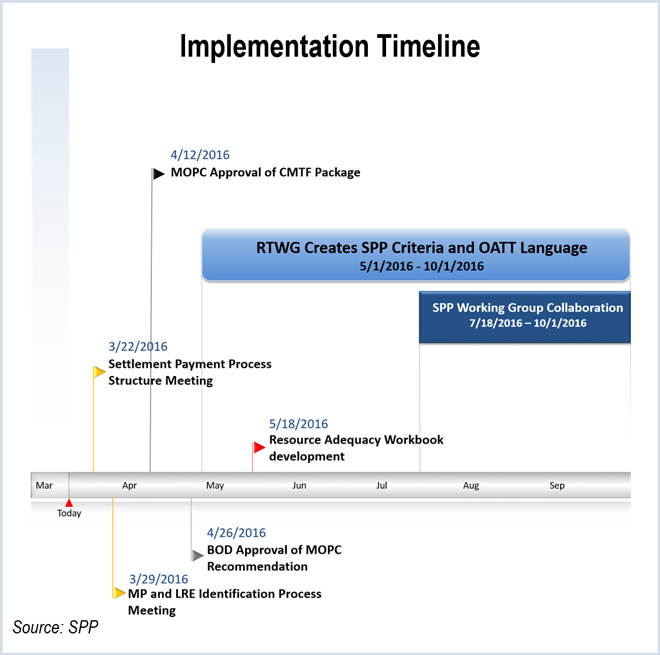
The SPP Capacity Margin Task Force conducted its penultimate meeting as it continues to set up the stakeholder group that will replace it.
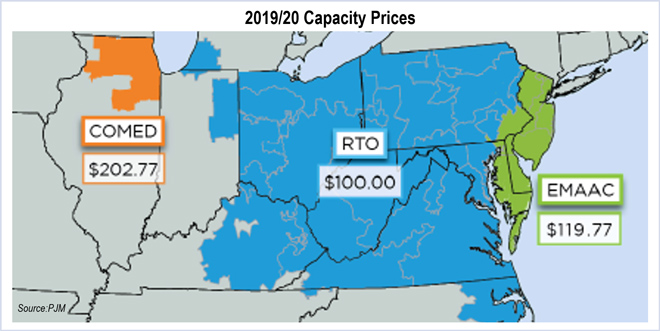
PJM Capacity prices fell sharply as new generation flooded the market, leaving 18 GW of existing resources without any capacity revenue.
ERCOT said continued growth in natural gas and renewable energy capacity will help it meet its projected summer peak this year.
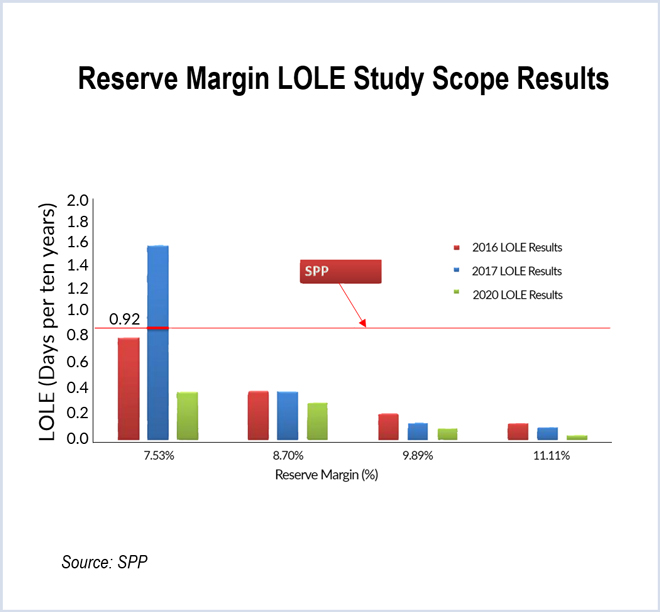
SPP members voted last week to reduce the RTO’s planning reserve margin to 12% from the current 13.6%.
MISO acknowledged that it missed its original goal of making a FERC filing in December, and now hopes for a May filing.
ERCOT said it continues to expect to have sufficient resources to meet projected peak-demand during the spring and summer.
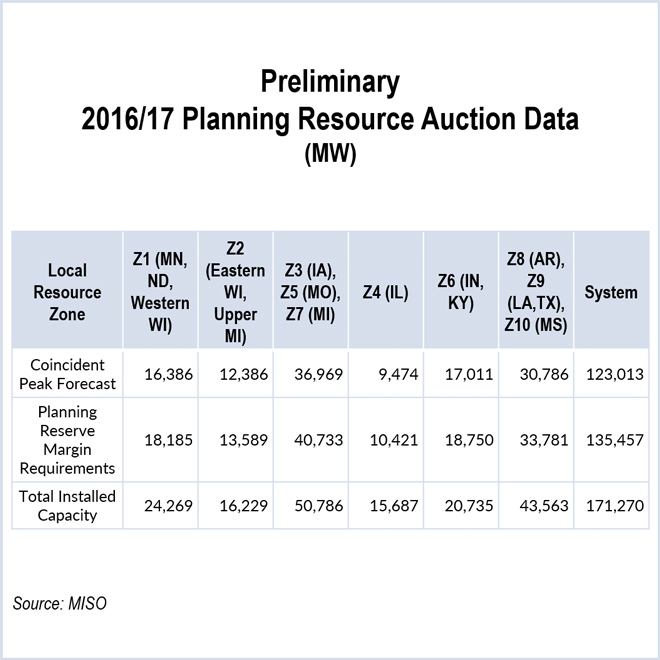
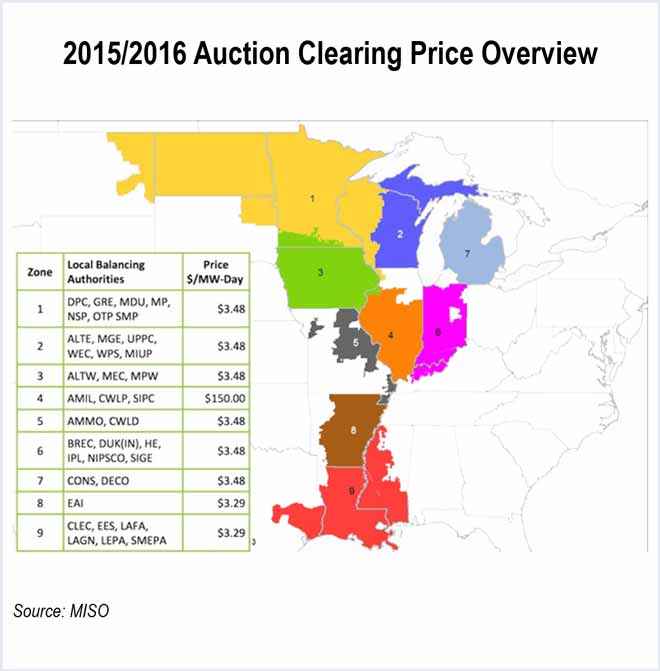
Dynegy and Exelon proposed that MISO Zone 4 procure capacity in three-year forward auctions separate from the rest of the RTO.
Reducing SPP’s current 13.6% reserve margin to 12% could cut required capacity by about 1,000 MW, saving $86 million annually and $1.3 billion over 40 years.
Want more? Advanced Search