Public Policy
Environmental RegulationsReliabilityState & RegionalAlabamaAlaskaArizonaArkansasCaliforniaColoradoConnecticutDelawareDistrict of ColumbiaFloridaGeorgiaHawaiiIdahoIllinoisIndianaIowaKansasKentuckyLouisianaMaineManitobaMarylandMassachusettsMichiganMinnesotaMississippiMissouriMontanaNebraskaNevadaNew HampshireNew JerseyNew MexicoNew YorkNorth CarolinaNorth DakotaOhioOklahomaOntarioOregonPennsylvaniaRhode IslandRTO-IndianaSouth CarolinaSouth DakotaTennesseeTexasUtahVermontVirginiaWashingtonWest VirginiaWisconsinWyoming
The winter of 2025/26 was the most expensive winter in the history of ISO-NE’s wholesale markets, driven by the lowest average temperatures in 20 years.
Kentucky lawmakers are working to overhaul the Public Service Commission in what they say is an effort to combat rising rates, while the governor characterized it as political maneuvering.
The New Jersey Board of Public Utilities approved the state’s first incentivized storage projects and launched new community and grid-scale solar solicitations.
No specifics are being offered, and the site’s owner indicates significant financial and political support must be established before such a restart of Indian Point could be considered.
Two Arizona utilities received approval to convert coal-fired power plants to run on natural gas, projects they say will enhance grid reliability, reduce emissions and preserve jobs.
Politicians increasingly are interested in wholesale markets, which has meant price caps but also is pushing regulators and the industry to move faster on meeting rising demand affordably and reliably.
Energy officials in Idaho, Utah and Wyoming called on the West-Wide Governance Pathways Initiative to ensure states with members in the Regional Organization for Western Energy have full access to data and market information, saying failure to do so risks infringing states’ rights and undermining public confidence.
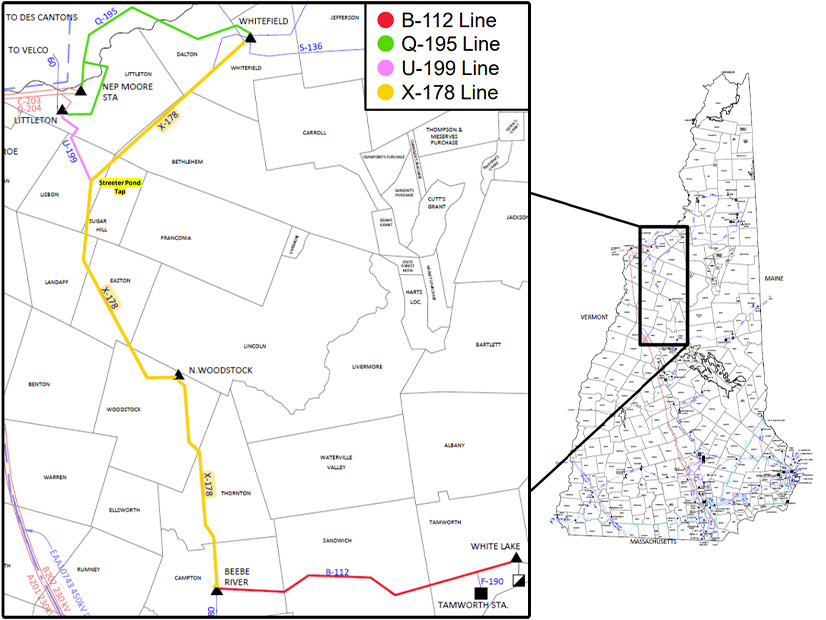
FERC dismissed a complaint about a $385 million asset condition project on an Eversource Energy transmission line in New Hampshire, finding it failed to demonstrate any violations by the company.
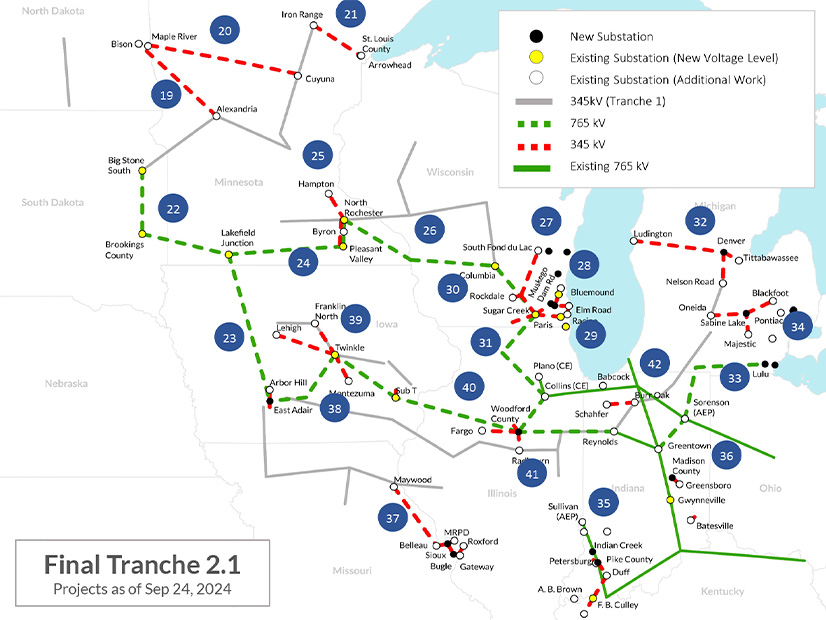
MISO opened a third review of a long-range transmission project, this time because three substations are needed more than five years ahead of schedule to accommodate new data center load.
The Senate Energy and Natural Resources Committee advanced FERC Commissioner David LaCerte’s nomination for a new, full five-year term by a vote of 12-8.
Want more? Advanced Search