Public Policy
Environmental RegulationsReliabilityState & RegionalAlabamaAlaskaArizonaArkansasCaliforniaColoradoConnecticutDelawareDistrict of ColumbiaFloridaGeorgiaHawaiiIdahoIllinoisIndianaIowaKansasKentuckyLouisianaMaineManitobaMarylandMassachusettsMichiganMinnesotaMississippiMissouriMontanaNebraskaNevadaNew HampshireNew JerseyNew MexicoNew YorkNorth CarolinaNorth DakotaOhioOklahomaOntarioOregonPennsylvaniaRhode IslandRTO-IndianaSouth CarolinaSouth DakotaTennesseeTexasUtahVermontVirginiaWashingtonWest VirginiaWisconsinWyoming
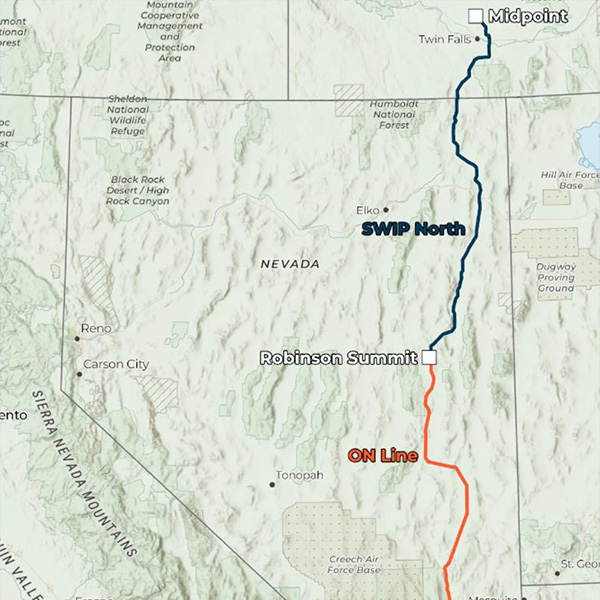
Nevada regulators approved a construction permit for the SWIP-North transmission line, keeping the project on track for a 2028 operation date.
As extreme winter weather descended on the Eastern U.S. and Canada, Hydro-Québec suspended power exports to New England on the New England Clean Energy Connect transmission line because of reliability concerns in Québec.
PJM presented manual revisions to clarify how resources are defined as offline for the purpose of determining whether they are eligible for lost opportunity cost credits.
PJM stakeholders kicked off discussions on creating a “backstop” auction to be held in September at the insistence of the Trump administration and the governors of the RTO’s 13 states.
The winter storm that moved through Texas and much of the Eastern Interconnection cut power to hundreds of thousands of people and stressed the bulk power system, but did not create major disruptions like other storms earlier this decade.
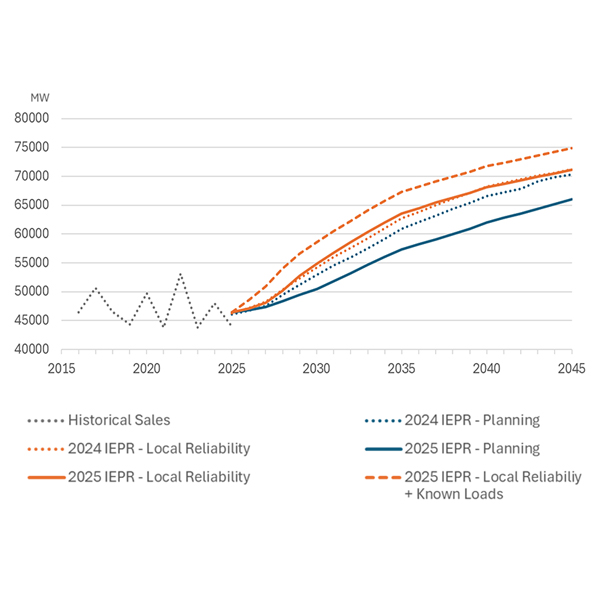
The California Energy Commission signed off on a forecast showing the state's electricity consumption could surge by as much as 61% over the next 20 years, mostly from increased EV adoption.
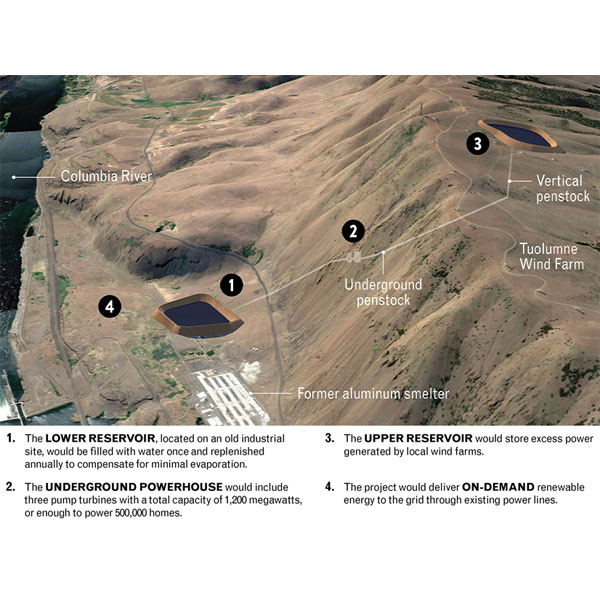
FERC approved a 40-year license for a proposed 1.2-GW pumped hydroelectric storage facility near the city of Goldendale in Klickitat County, Wash.
The four aging reactors and their 3.36 GW of output are considered an indispensable part of New York’s power portfolio and decarbonization strategy.
U.S. Energy Secretary Chris Wright said the department is ready to use its authority under Section 202(c) of the Federal Power Act to dispatch backup generation from large customers if needed ahead of a major winter storm.
FERC addressed the ongoing resource adequacy challenges at PJM during its regular meeting, calling for the RTO to get reforms in front of it so they can be approved.
Want more? Advanced Search